第一讲 基础算法
1. 前缀和
二维前缀和就是可以O(1)时间内求出任意两点组成的矩形的所有元素的和
acwing 796. 子矩阵的和 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/798/
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(), m = sc.nextInt(), q = sc.nextInt();
int[][] arr = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
arr[i][j] += arr[i - 1][j] + arr[i][j - 1] - arr[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int x1 = sc.nextInt(), y1 = sc.nextInt(), x2 = sc.nextInt(), y2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(arr[x2][y2] - arr[x2][y1 - 1] - arr[x1 - 1][y2] + arr[x1 - 1][y1 - 1]);
}
sc.close();
}
}2. 差分
差分:需要构建一个数组,使得新数组的前缀和数组为原数组
这样就能在O(1)时间内完成某个区间的每个元素都加上C(通过差分数组的两端点:+C和-C)
acwing 797. 差分 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/799/
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(), m = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int[] dif = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dif[i] = arr[i] - arr[i - 1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int L = sc.nextInt(), R = sc.nextInt(), C = sc.nextInt();
dif[L] += C;
if (R + 1 <= n)
dif[R + 1] -= C;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dif[i] += dif[i - 1];
}
//输出
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.print(dif[i] + " ");
}
sc.close();
}
}二维差分:
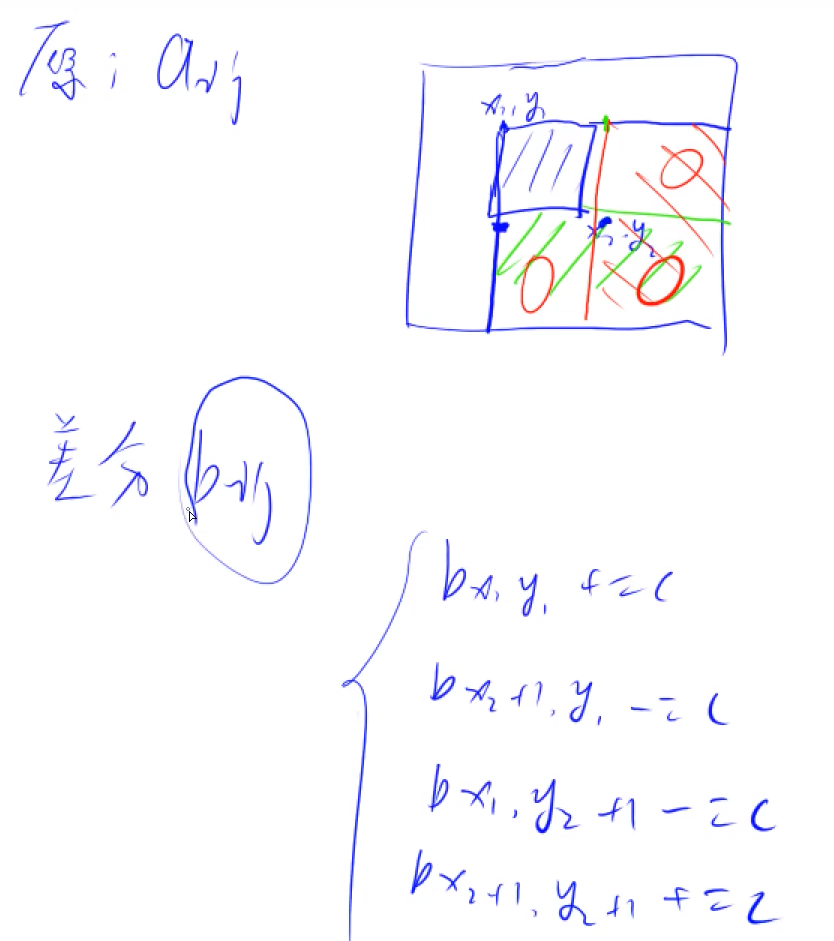
acwing 798. 差分矩阵 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/800/
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(), m = sc.nextInt(), q = sc.nextInt();
int[][] arr = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
int[][] dif = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
dif[i + 1][j + 1] = arr[i + 1][j + 1] - arr[i + 1][j] - arr[i][j + 1] + arr[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int x1 = sc.nextInt(), y1 = sc.nextInt(), x2 = sc.nextInt(), y2 = sc.nextInt(), c = sc.nextInt();
dif[x1][y1] += c;
if (x2 + 1 <= n)
dif[x2 + 1][y1] -= c;
if (y2 + 1 <= m)
dif[x1][y2 + 1] -= c;
if (x2 + 1 <= n && y2 + 1 <= m)
dif[x2 + 1][y2 + 1] += c;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
dif[i][j] += dif[i][j - 1] + dif[i - 1][j] - dif[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
System.out.print(dif[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}3. 离散化
由于数据范围太大(如果为了O(1)访问,直接开大数组会内存溢出),因此将这些数通过排序映射到0, 1 , 2, 3... n,这样就能用O(logN)的时间得到原数的映射(即下标)
类似于哈希
acwing 802. 区间和 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/804/
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static class Pair {
int L;
int R;
Pair(int L, int R) {
this.L = L;
this.R = R;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(), m = sc.nextInt();
List<Pair> adds = new ArrayList<>();
List<Pair> qureys = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Integer> idxSet = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x = sc.nextInt(), c = sc.nextInt();
adds.add(new Pair(x, c));
idxSet.add(x);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int l = sc.nextInt(), r = sc.nextInt();
idxSet.add(l);
idxSet.add(r);
qureys.add(new Pair(l, r));
}
List<Integer> idxs = new ArrayList<>(idxSet);
Collections.sort(idxs);
int N = idxs.size();
int[] arr = new int[N + 1];
for (Pair add : adds) {
arr[find(idxs, add.L)] += add.R;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
arr[i] += arr[i - 1];
}
for (Pair qurey : qureys) {
System.out.println(arr[find(idxs, qurey.R)] - arr[find(idxs, qurey.L) - 1]);
}
sc.close();
}
public static int find(List<Integer> list, int x) {
int L = 0, R = list.size() - 1;
while (L <= R) {
int mid = L + (R - L) / 2;
if (list.get(mid) < x) {
L = mid + 1;
} else if (list.get(mid) > x) {
R = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid + 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
}